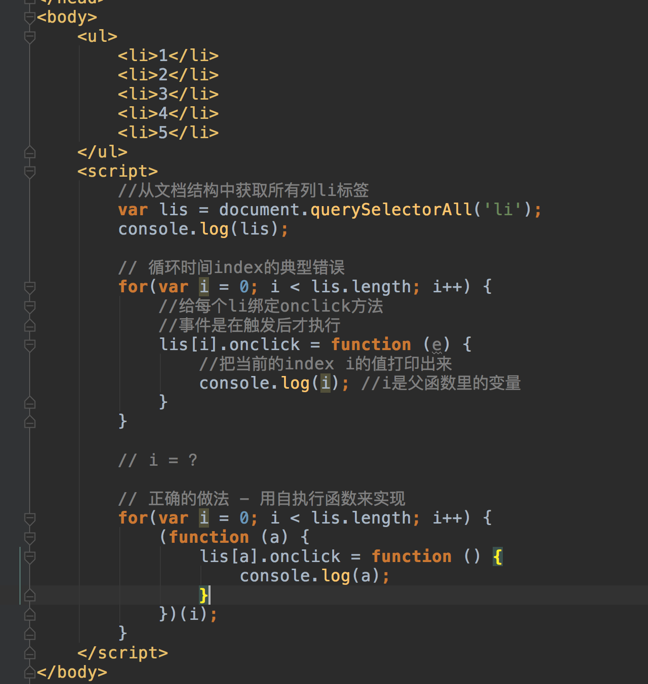
Scope chain
In JavaScript there are two types of scope:
- Local scope
- Global scope
JavaScript has function scope: Each function creates a new scope.
Scope determines the accessibility (visibility) of these variables.
Variables defined inside a function are not accessible (visible) from outside the function.
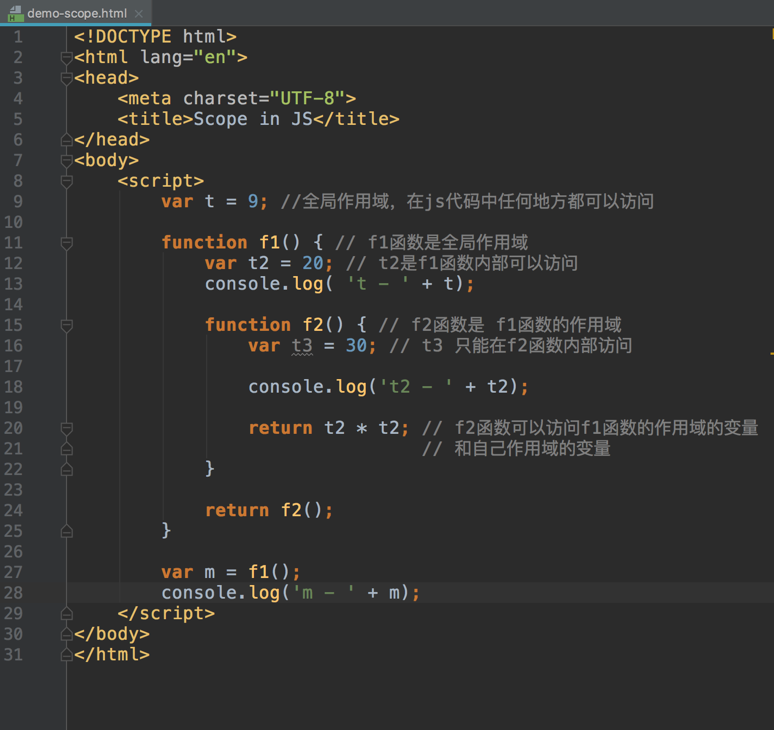
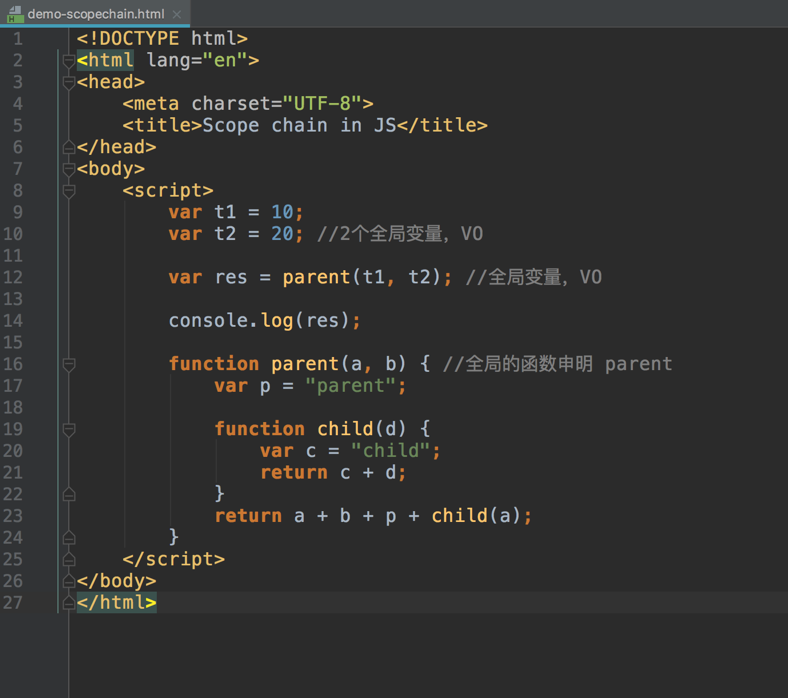
Scope chain
The scope chain property of each execution context is simply a collection of the current context variable object + all parent’s lexical variable objects.
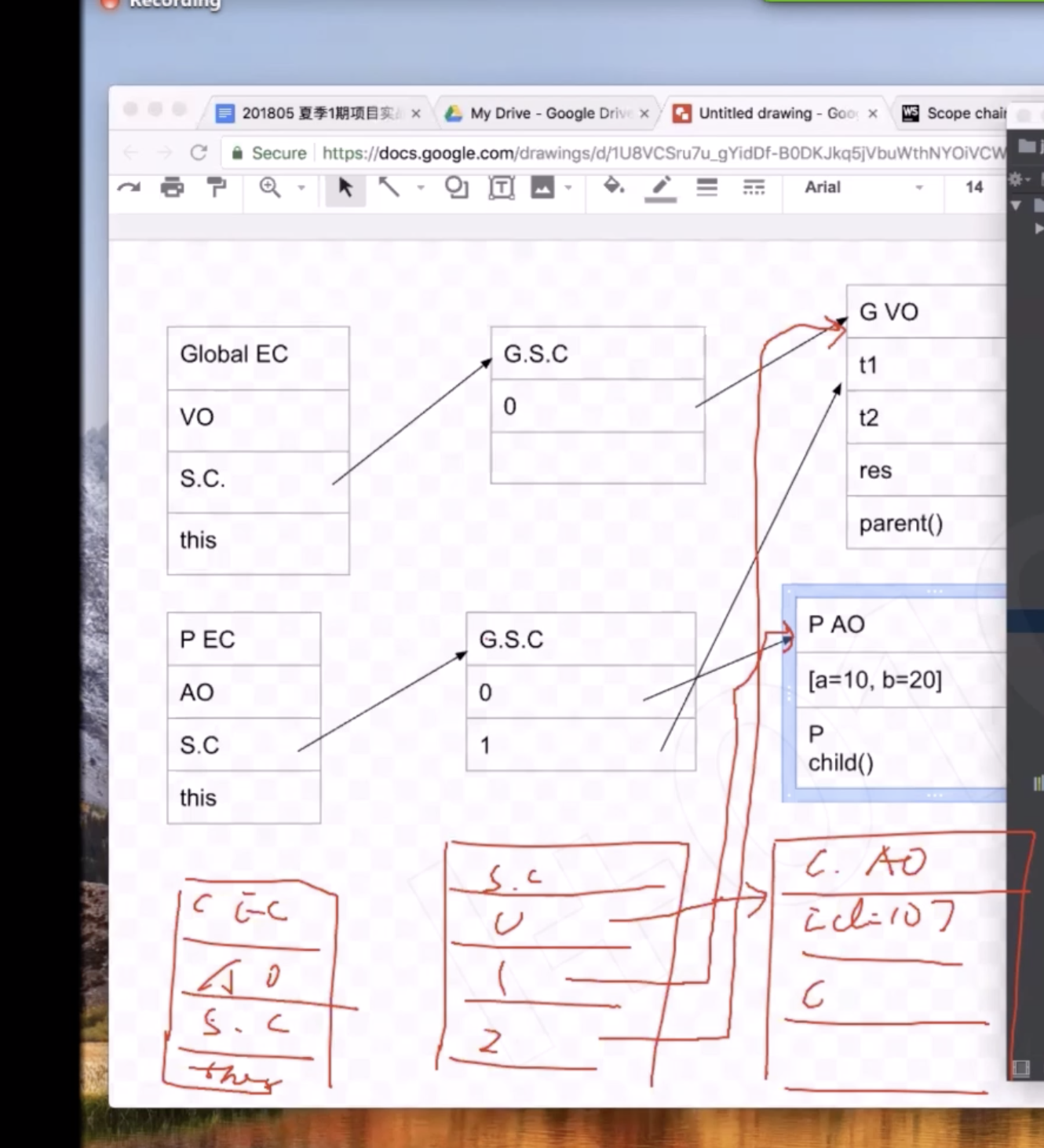
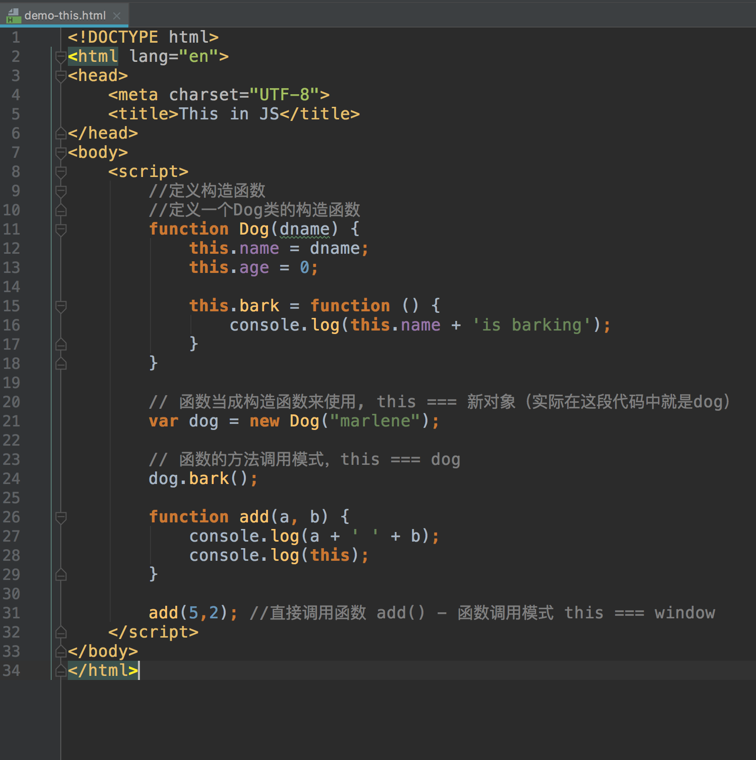
this in JavaScript
1 | <script> |
Closure
Definition
A closure is a function having access to the parent scope, even after the parent function has closed.
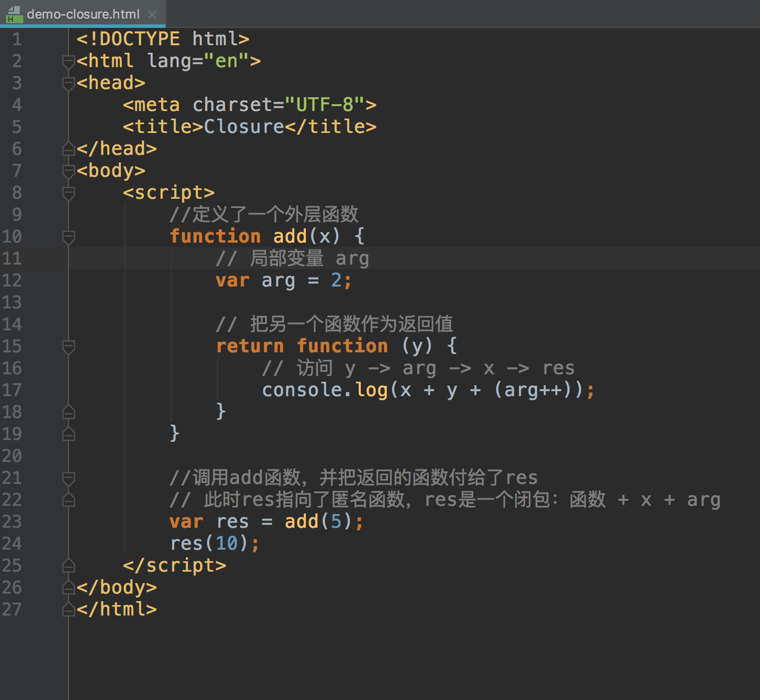
Closure here includes the annonymous function and the local variable arg. Here the local variable won’t be released even add() is ended.
examples: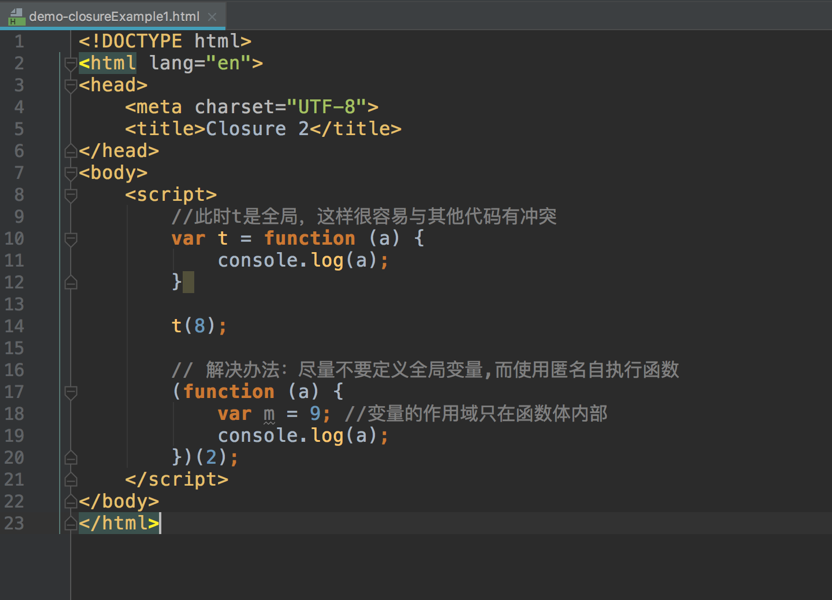
BOM & DOM
BOM
There are no official standards for the Browser Object Model (BOM).
Since modern browsers have implemented (almost) the same methods and properties for JavaScript interactivity, it is often referred to, as methods and properties of the BOM.
The BOM (Browser Object Model) consists of the objects navigator, history,screen, location and document which are children of window
DOM
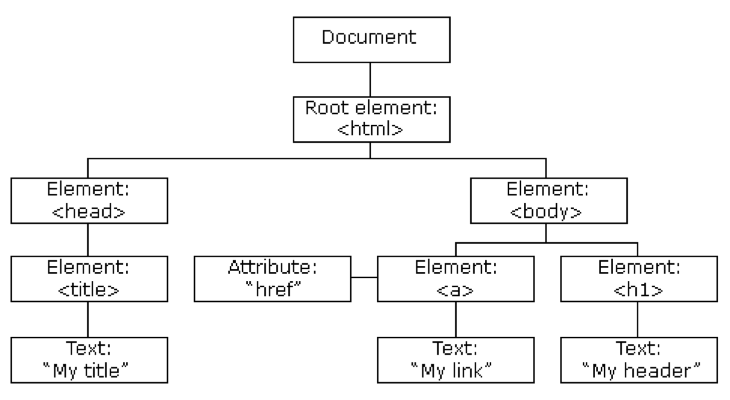
The Document Object Model (DOM) connects web pages to scripts or programming languages. Usually that means JavaScript. The DOM model represents a document with a logical tree. DOM methods allow programmatic access to the tree; with them you can change the document’s structure, style or content. DOM nodes can have event handlers attached to them. Once an event is triggered, the event handlers get executed.
Document Object
- When an HTML document is loaded into a web browser, it becomes a document object.
- The document object is the root node of the HTML document.
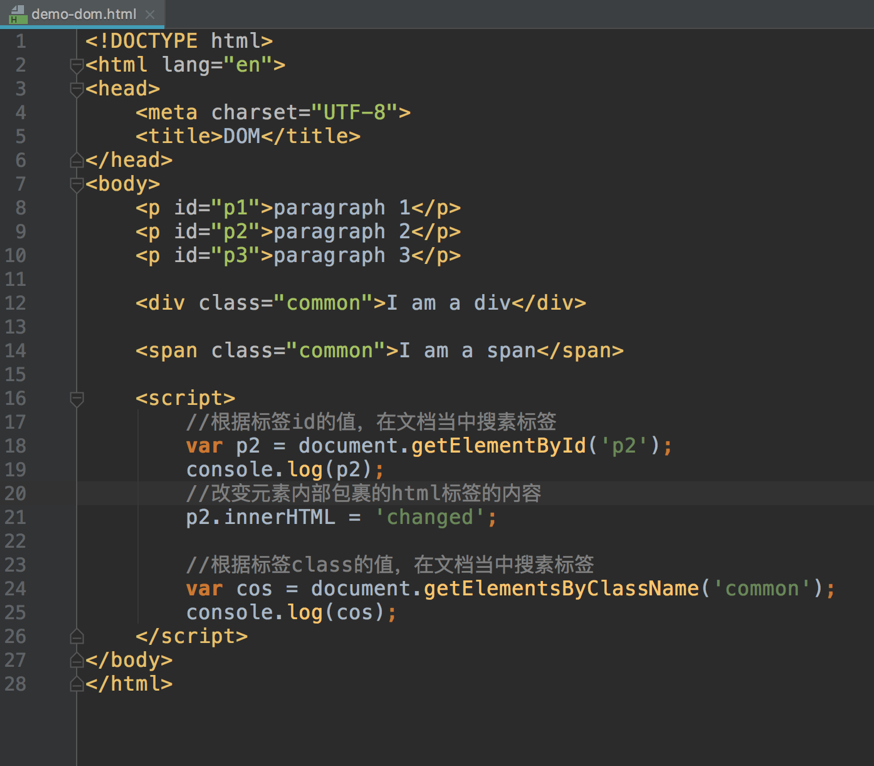
Finding HTML Elements
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| document.getElementById(id) | Find an element by element id |
| document.getElementsByTagName(name) | Find elements by tag name |
| document.getElementsByClassName(name) | Find elements by class name |
Changing HTML Elements
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| element.innerHTML = new html content | Change the inner HTML of an element |
| element.attribute = new value | Change the attribute value of an HTML element |
| element.setAttribute(attribute, value) | Change the attribute value of an HTML element |
| element.style.property = new style | Change the style of an HTML element |
Adding and Deleting Elements
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| document.createElement(element) | Create an HTML element |
| document.removeChild(element) | Remove an HTML element |
| document.appendChild(element) | Add an HTML element |
| document.replaceChild(element) | Replace an HTML element |
| document.write(text) | Write into the HTML output stream |
Event
Capturing phase– the event goes down to the element.Bubbling phase– the event bubbles up from the element.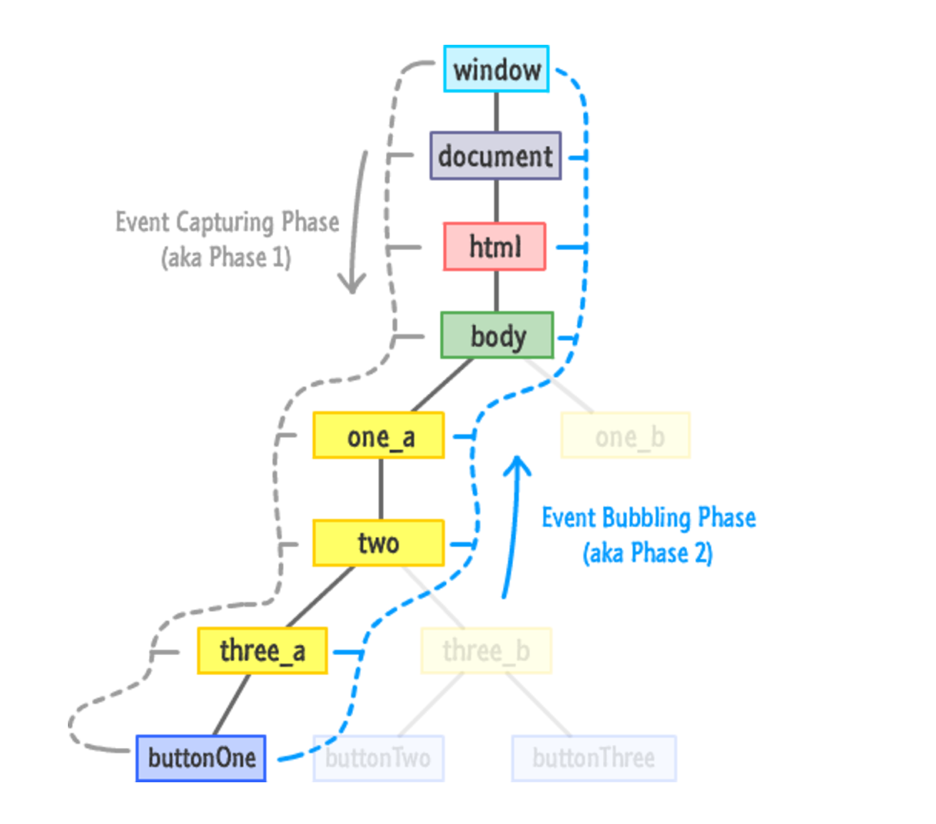
DOM0 - onclick
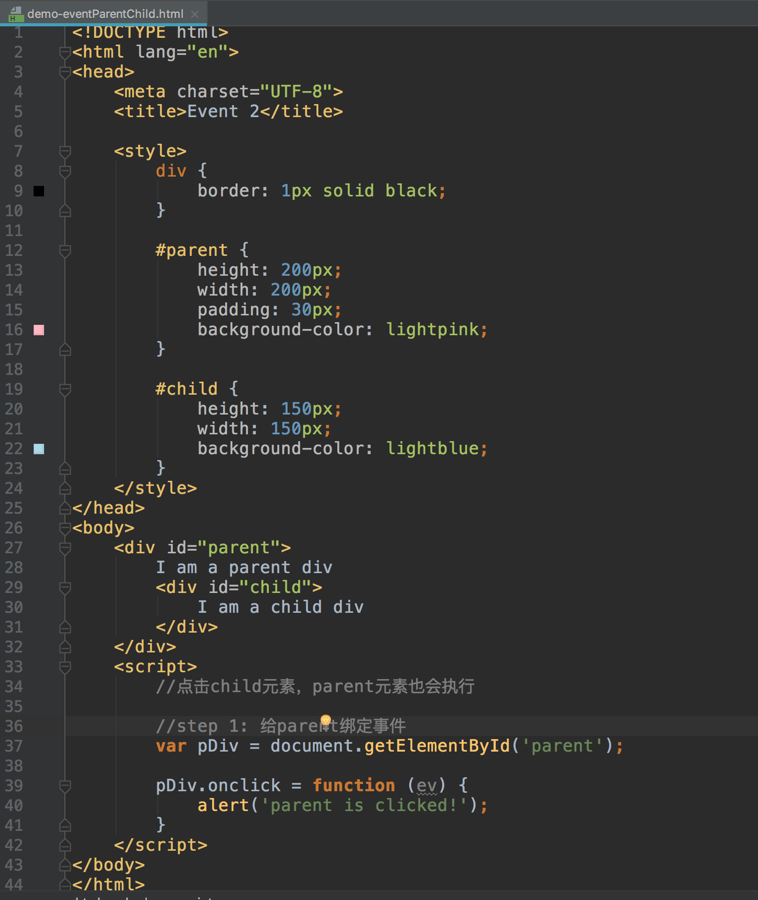
Don’t write JS code inline.
DOM2 - addEventListener
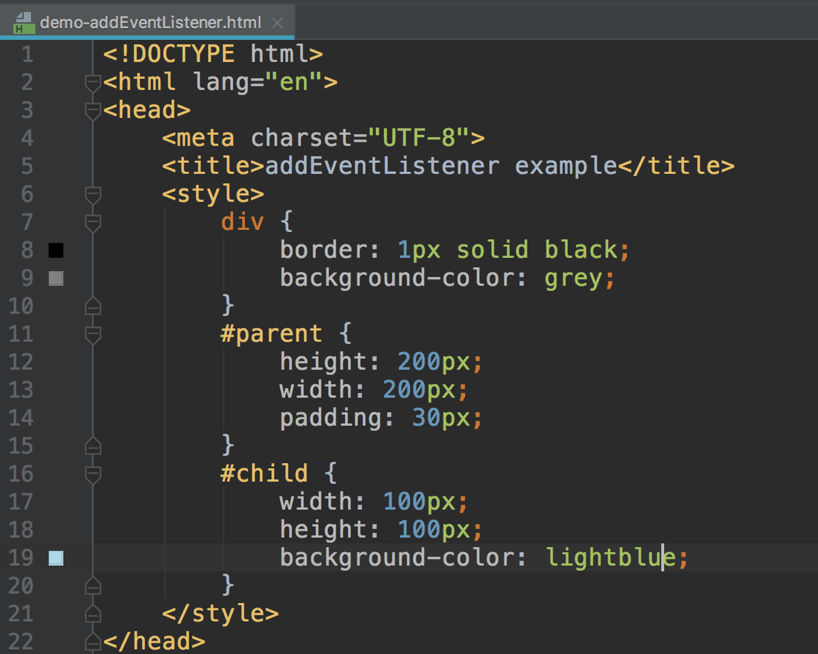
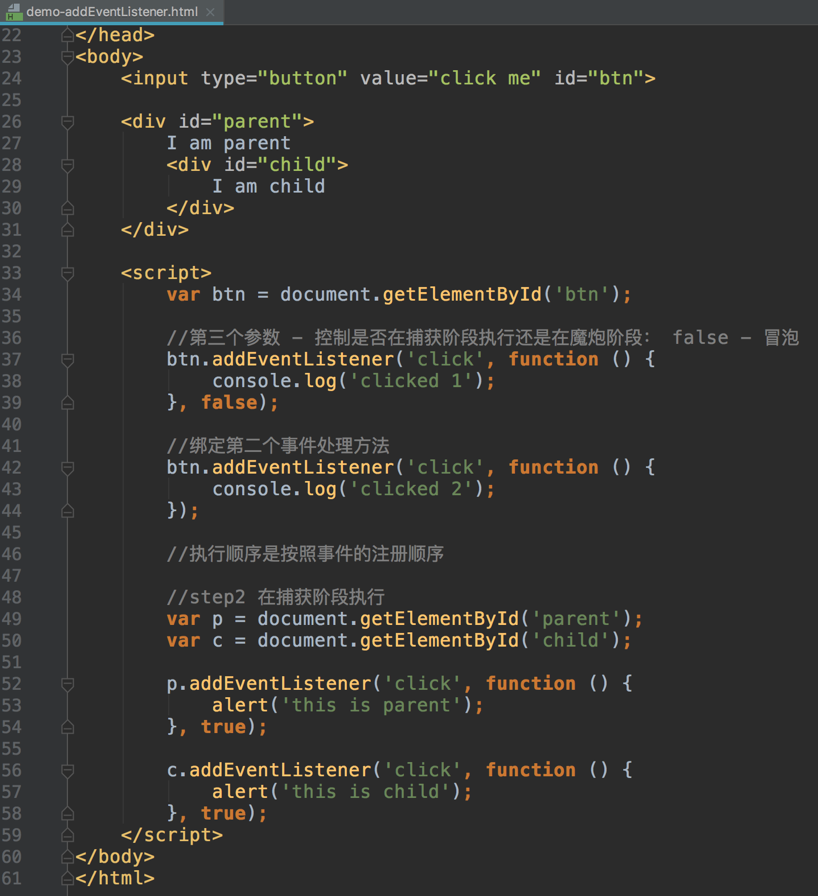
捕获阶段与冒泡阶段区别在于谁先触发
Example: